How to Source Fusible Interlining in Bulk for Garment Production?

Modern garment manufacturing relies on fusible interlining technology to achieve professional quality while maintaining production efficiency. This article serves as a comprehensive resource on fusible interlining, explaining its purpose, features, and terminology. This specialized textile component combines a fabric substrate with heat-activated adhesive coating, revolutionizing how manufacturers approach garment construction from traditional needle and thread methods to advanced thermoplastic bonding processes.
For garment factories, brands, and wholesale buyers, understanding fusible interlining selection, application parameters, and sourcing considerations directly impacts product quality, production costs, and manufacturing efficiency. Selecting the right fusible interlining is crucial for the success of any garment manufacturing or sewing project, whether it involves dressmaking, bag making, quilting, or home decor. This comprehensive guide covers everything from basic terminology to bulk procurement strategies, enabling informed decisions that maintain professional standards while optimizing production workflows.
What is Fusible Interlining
Fusible interlining represents a fabric substrate engineered with heat-activated adhesive coating applied to one or both sides, designed to provide structure, stability, and shape retention in garment construction. The adhesive coating consists of tiny glue dots that melt with heat, bonding the interlining to the fabric. Unlike traditional interlining that requires stitching attachment, fusible interlining bonds directly to outer fabric through controlled heat and pressure application, eliminating the need for additional sewing operations.
The primary function centers on creating dimensional stability in specific garment areas while maintaining desired drape characteristics and hand feel. This bonding creates what manufacturers term a “fused” state where the interlining and outer fabric become mechanically joined through thermoplastic adhesive activation.
The key difference from non-fusible interlining lies in the thermoplastic bonding process, which enables faster production cycles and consistent quality control compared to labor-intensive hand-stitching methods. Modern adhesive chemistry allows precise temperature activation ranges, ensuring reliable bonds that withstand washing, dry cleaning, and extended wear cycles.
Critical applications in modern garment manufacturing include collar and cuff reinforcement, shirt front stabilization, jacket panel construction, and waistband support. The technology has become essential for maintaining professional appearance standards while achieving cost-effective production scaling.
Types of Fusible Interlining by Construction
Different construction methods produce distinct performance characteristics, making proper selection crucial for achieving desired garment properties and production efficiency.
|
Construction Type |
Weight Range (GSM) |
Primary Applications |
Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Woven |
25-120 |
Formal wear, suits, structured garments |
Maximum stability, crisp edges |
|
Non-Woven |
20-150+ |
Casual wear, sportswear, mass production |
Cost-effective, versatile weight options |
|
Knitted |
30-80 |
Activewear, stretch garments, fitted items |
Stretch properties, recovery characteristics |
|
Tricot |
25-60 |
High-end fashion, curved seams, draping |
Dimensional stability with flexibility |
When using fusible interlining, it is important to adjust the size of the interlining so it is slightly smaller than the fabric pieces. This helps ensure a proper fit and prevents excess bulk in the finished garment.
Woven Fusible Interlining
Woven construction delivers exceptional fabric stability through traditional weaving processes, making it ideal for applications requiring crisp, defined edges and professional appearance. Weight ranges from lightweight 25 GSM options for delicate shirt applications to heavyweight 120 GSM specifications for structured outerwear and formal jackets.
Manufacturing utilizes standard weaving machinery with cotton, polyester, or blended yarn systems depending on end-use requirements. The woven structure provides consistent dimensional stability across both warp and weft directions, essential for maintaining shape in collar points, cuff edges, and front plackets.
Applications in formal wear include suit jacket fronts, dress shirt collars, trouser waistbands, and anywhere crisp definition enhances professional appearance. The grain direction becomes critical during pattern cutting, requiring careful alignment with outer fabric grain for optimal fusing results and dimensional stability. It is important to accurately cut the interlining along the correct grain to ensure proper fit and to avoid excess bulk in finished garments.
Quality considerations include thread count specifications, yarn denier selection, and weave density optimization for target weight and drape characteristics. Premium applications may specify cotton warp with polyester weft for enhanced performance across different coating chemistries.
Non-Woven Fusible Interlining
Non-woven manufacturing processes utilize polyester or polypropylene fibers arranged in multidirectional patterns without traditional weaving or knitting operations. This construction method enables significant cost advantages while providing versatile performance across lightweight 20 GSM to heavy-duty 150+ GSM specifications.
Production efficiency benefits include faster manufacturing cycles, reduced raw material costs, and simplified inventory management through standardized weight offerings. The fiber arrangement can be optimized for specific applications, with random orientation providing balanced stability or parallel/cross-laid arrangements offering directional properties.
Weight variations accommodate diverse applications from lightweight shirt reinforcement to heavy-duty outerwear construction. Medium weights around 60-80 GSM represent the most versatile options for general garment manufacturing, balancing structure with cost considerations.
Applications in casual wear, sportswear, and mass production benefit from consistent quality characteristics and competitive pricing. The absence of yarn interlacement reduces bulk while maintaining adequate bonding surface for reliable adhesive activation across different coating systems.
Adhesive Coating Technologies
Modern adhesive coating chemistry determines bonding characteristics, temperature requirements, and performance parameters essential for successful production operations. Selection criteria must balance fabric compatibility, wash durability requirements, and manufacturing equipment capabilities.
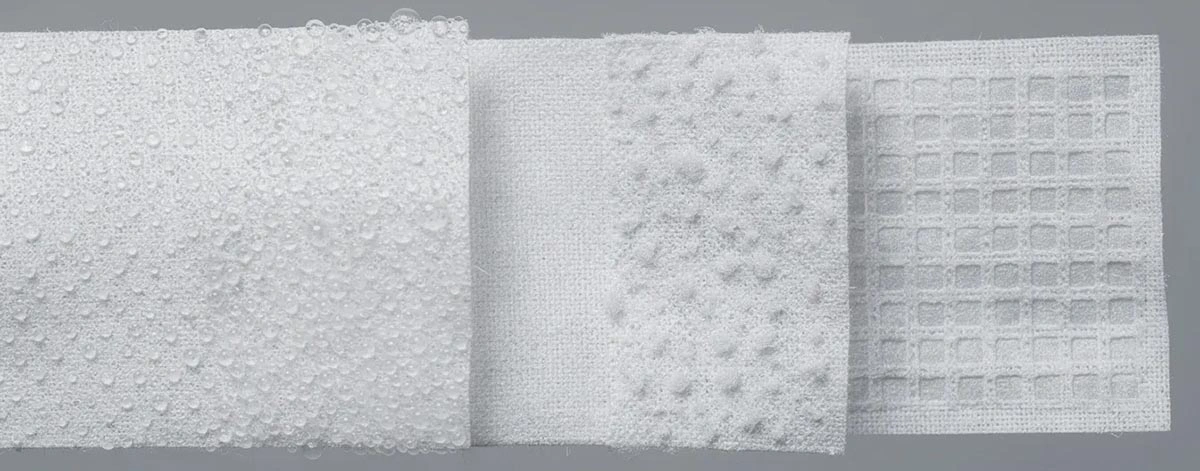
Coating application methods include dot patterns for controlled coverage, powder distribution for even bonding, and web application for maximum adhesion area. Each method influences final product characteristics including hand feel, bonding strength, and cost structure.
Polyamide (PA) Coatings
Polyamide coating systems require higher temperature activation typically ranging 130-150°C with excellent wash durability and permanent bonding characteristics. The chemistry provides strong initial tack during fusing operations with superior resistance to repeated washing cycles and dry cleaning solvents.
Temperature requirements demand equipment capable of precise control within the activation range while protecting outer fabrics from heat damage. Proper calibration ensures complete adhesive activation without compromising fabric integrity or causing dimensional changes.
Applications ideal for formal wear, outerwear, and heavy-duty garments benefit from the exceptional bond strength and durability characteristics. Professional garments requiring repeated dry cleaning cycles particularly benefit from the solvent resistance properties inherent in polyamide chemistry.
Resistance to dry cleaning solvents makes PA coatings essential for garments requiring commercial cleaning services. The higher activation temperature also provides resistance to accidental adhesive reactivation during steam pressing or finishing operations.
Polyester (PES) Coatings
Polyester coating systems operate at lower fusing temperatures ranging 110-130°C, making them suitable for delicate fabrics that cannot tolerate higher heat levels. The chemistry provides good wash resistance with moderate bond strength, offering cost-effective solutions for mass production applications.
Lower temperature requirements expand fabric compatibility to include heat-sensitive materials while reducing energy consumption during production operations. Equipment requirements become less demanding, enabling broader implementation across diverse manufacturing facilities.
Cost-effective positioning makes PES coatings attractive for mass production and casual wear applications where moderate performance meets requirements without premium pricing. The chemistry balances adequate performance with economic considerations for competitive manufacturing.
Compatibility with synthetic and natural fiber blends enables versatile application across diverse fabric types. The moderate bonding characteristics provide adequate performance for most casual garment applications while maintaining cost competitiveness.
EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate) Coatings
EVA coating chemistry provides flexible bonding with soft hand feel characteristics, operating in temperature ranges 120-140°C with good repositioning ability during application. The chemistry creates bonds that maintain flexibility after cooling, preserving fabric drape and comfort properties.
Flexible bonding characteristics make EVA coatings ideal for sportswear, children’s wear, and comfort garments where maintaining soft hand feel takes priority over maximum bond strength. The chemistry accommodates fabric movement without creating stiff or rigid areas.
Temperature range specifications provide operational flexibility while maintaining reliable bonding across different fabric weights and types. Good repositioning ability allows minor adjustments during fusing operations, reducing waste and improving production efficiency.
Applications in sportswear benefit from excellent adhesion to technical fabrics and performance materials. The coating chemistry maintains bond integrity during moisture exposure and repeated washing cycles typical in athletic wear applications.
PU (Polyurethane) Coatings
Polyurethane represents premium coating chemistry with exceptional flexibility and durability, operating at low temperatures ranging 90-110°C suitable for heat-sensitive fabrics. The chemistry provides superior wash resistance and dry cleaning compatibility for high-end applications.
Low-temperature fusing capabilities enable application to delicate fabrics including silk, fine wool, and specialty synthetic materials that require careful temperature control. Equipment requirements remain accessible while expanding application possibilities.
Superior wash resistance maintains bond integrity through extended care cycles, making PU coatings suitable for garments requiring frequent laundering or commercial cleaning services. The chemistry resists degradation from detergents and cleaning solvents.
High-end applications requiring premium performance benefit from the exceptional flexibility and durability characteristics. Luxury garments, professional wear, and specialty applications justify the premium cost through enhanced performance and customer satisfaction.
Production Applications and Selection Guidelines
Strategic application selection requires matching interlining specifications to functional requirements, fabric characteristics, and quality expectations. It is important to carefully select the appropriate fusible interlining for each garment application to ensure the best results. Systematic evaluation ensures optimal performance while maintaining cost efficiency.
Application-specific requirements include weight specifications, coating chemistry, construction type, and compatibility considerations for achieving professional results across diverse garment categories. In each case, the choice of interlining depends on the specific requirements of the garment and its intended use.
Collar and Cuff Reinforcement
Medium to heavyweight woven interlining ranging 60-100 GSM provides essential structure for maintaining crisp appearance and professional definition in collar points and cuff edges. Cuffs, like collars, benefit from the added structure provided by fusible interlining, which helps them maintain their shape and support the garment's overall structure. Weight selection depends on outer fabric characteristics and desired stiffness levels.
PA or PU coatings deliver the durability necessary for withstanding repeated washing and professional cleaning cycles typical in business and formal wear. Bond strength requirements exceed casual wear applications due to stress concentrations at collar points and cuff edges.
Grain matching requirements demand careful attention during cutting operations, ensuring interlining grain aligns with outer fabric for optimal fusing results and dimensional stability. Mismatched grain orientation can cause puckering or distortion during application.
Quality benchmarks include shape retention after multiple wash cycles, crease resistance during wear, and maintained collar point definition. Professional appearance standards require consistent performance across production lots and extended garment life.
Shirt Fronts and Plackets
Lightweight to medium weight specifications ranging 25-60 GSM maintain structural support while preserving the soft drape characteristics essential in dress shirts and casual garments. Weight selection balances support with comfort considerations.
Woven or tricot construction preserves drape characteristics while providing adequate stability for buttonhole reinforcement and front panel definition. The construction choice influences both performance and cost considerations in large production runs.
PES or EVA coatings provide soft hand feel essential for garments worn against skin while delivering adequate bonding for normal wear and care cycles. Temperature compatibility accommodates diverse fabric types common in shirt manufacturing.
Buttonhole reinforcement considerations require additional evaluation of interlining placement and weight to ensure adequate support without creating thick, uncomfortable areas around button placement zones.
Jacket Front Panels and Lapels
Heavy-duty woven interlining specifications ranging 80-120 GSM provide the structural support necessary for maintaining professional silhouette and shape definition in structured jackets and outerwear. Weight selection depends on garment style and target market positioning.
PA coating systems deliver permanent bonding essential for garments requiring extended wear cycles and repeated cleaning services. The chemistry provides the durability necessary for investment garments where longevity justifies premium costs.
Canvas replacement applications benefit from modern fusible technology, eliminating labor-intensive hand-padding operations while maintaining traditional tailoring appearance. Production efficiency gains enable competitive pricing without sacrificing quality standards.
Shape memory requirements ensure garments maintain intended silhouette through extended wear and multiple cleaning cycles. Professional appearance standards demand consistent performance that meets customer expectations for business and formal wear.
Waistbands and Belts
High-density non-woven specifications ranging 100-150+ GSM provide the rigidity necessary for maintaining waistband shape and preventing roll during wear. Weight selection accommodates diverse garment styles from casual to formal applications.
Double-sided fusible options eliminate additional construction steps by providing adhesive coating on both surfaces, enabling efficient attachment to both garment body and facing materials simultaneously. Production efficiency benefits include reduced handling and processing time.
PA or PU coatings deliver maximum durability for high-stress applications where waistbands experience repeated flexing and stretching during wear. Bond strength requirements exceed other garment areas due to mechanical stress concentrations.
Width stability and curl resistance specifications ensure waistbands maintain intended appearance and comfort throughout garment life. Quality standards include resistance to rolling, puckering, or dimensional changes during normal wear conditions.
Fusible interlining is also widely used in bag making to provide structure and support to bag panels and linings.
Fabric Compatibility and Testing
Systematic evaluation procedures ensure optimal interlining selection while validating performance characteristics before full production implementation. Compatibility assessment is essential for a wide range of textiles used in garment manufacturing, as it reduces quality risks and enables confident scaling across large production volumes.
Testing protocols establish baseline performance metrics while identifying potential issues before they impact production schedules or customer satisfaction. Pre-production validation provides the foundation for consistent quality delivery.
Bulk Sourcing and Quality Assurance
Fusible interlining is commonly sold on rolls and in bulk quantities for manufacturing, making it suitable for large-scale production. The process of placing an order for fusible interlining involves communicating requirements to the supplier, and efficient order management is crucial to ensure timely delivery and fulfillment. The amount you pay for fusible interlining depends on factors such as quality, quantity, and the supplier you choose.
Quality assurance protocols establish performance standards while providing verification procedures that ensure consistent delivery across large volume orders. Standards development considers application requirements and customer expectations.
MH Fusible Interlining Solutions
MH’s comprehensive fusible interlining product range encompasses all major construction types and coating chemistries to support diverse garment manufacturing requirements. Our manufacturing capabilities combine advanced equipment with stringent quality control systems to deliver consistent performance across large production volumes.
Manufacturing capabilities include specialized coating equipment for precise adhesive application, comprehensive testing facilities for performance validation, and flexible production systems that accommodate both standard specifications and custom requirements. Our technical team provides application support throughout the product development and production scaling process.
Customization options enable OEM and ODM solutions tailored to specific fabric combinations, performance requirements, and application challenges. Custom development includes adhesive selection, coating weight optimization, construction modifications, and specialized testing protocols that ensure optimal performance for unique applications.
Ready to optimize your garment manufacturing with professional fusible interlining solutions? Contact MH today for comprehensive technical support, bulk sourcing options, and customized solutions tailored to your specific production requirements. Our team of experts stands ready to deliver the quality, reliability, and technical expertise your manufacturing operations demand.
Whether you need standard specifications for efficient production scaling or custom formulations for specialized applications, MH provides the fusible interlining solutions that maintain your quality standards while optimizing production costs. Discover how our advanced manufacturing capabilities and technical support can enhance your competitive positioning in today’s demanding marketplace.


